For most of us, our understanding of the printing process is limited to, ‘the blank card goes in here and the finished card comes out here.' This is a testament to the reliability of these printers—they work so we don't have to know how they work. However, as any mid- to high-volume user will tell you, a little understanding can go a long way when students are lined up and a printer has broken down.
The process used by most card printers today is called ‘dye diffusion thermal transfer' or ‘dye sublimation' (dye sub). It involves the transfer of dyes from a ribbon to a plastic card via heat. The key pieces of this process are the print head and the ribbon.
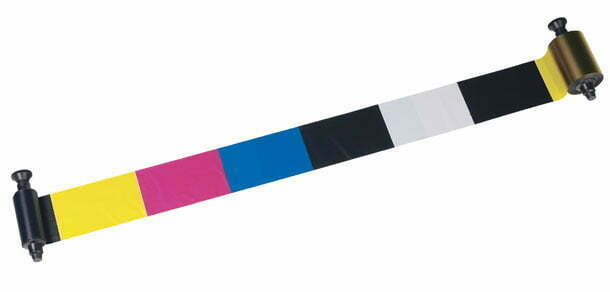
The base for a dye sub printer ribbon is a thin, but durable, plastic sheet called a carrier film. The carrier film is stained with a waxy substance containing the dyes. In color processes, the ribbon has a series of different colored panels which, when combined in specific amounts on the card, create the full spectrum of colors. The printer applies the dye from these panels, one pass at a time. Most ribbons utilize four panels for applying images and text–cyan, magenta, yellow, and black–and another clear panel that serves as a protective overlay. With these distinct color panels, all colors in the visible spectrum can be created.
To envision the process, think of a painter mixing colors on a palette. A certain portion of cyan mixed with yellow will produce a green hue. Add more cyan and an aqua will emerge. The key is in how are the colors applied in different and controlled proportions. The answer leads us to a discussion of print heads.
The print head is the means by which the heat is applied to the ribbon, at specified locations and at specified temperatures, to produce the intended color transfers to the card. A typical print head consists of 6 separate heating elements per millimeter. Each element is capable of producing 256 temperature variations. Each variation transfers a corresponding amount of dye from the ribbon to the card. As an example, a mid-range temperature from an element transfers a mid-range intensity of dye from the color panel to the card.
Each element creates or transfers dye to a single pixel or dot. Most card printers in use today print at 300 dots per inch (dpi). This means that in every square inch of card space, there are 9000 individual pixels (300 x 300). To create the accurate color specified in an image, a pixel may need dye from all three (or more in four and five panel ribbons) separate panels. As you can see, the printer must be a highly precise and reliable piece of equipment to control this process.
The majority of the card printers used on campuses are manufactured by Fargo, DataCard, Eltron, DaiNippon (DNP), Nisca, or one of handful of other makers. While most manufacturers will sell direct to end users, campuses frequently obtain printers via system integrators or resellers.
Each manufacturer offers a series of models with different feature sets. The key features to consider include:
How much time does it take for the printer to accept data and produce a finished card? Be aware that the time listed by the manufacturer can vary greatly when placed in your operating environment. Talk to users of the printer to get their impression of the actual print speed.
This is the printer's ability to print both sides of a card in the same print cycle. For many campuses, this feature is unnecessary as the back of the card will be preprinted by the card supplier or via another print station.
Nearly every printer has this capability but it is not always included in the price of the printer. Make sure that you find out if this module adds any additional costs to the unit.
Few campuses require this capability and this module typically carries an additional cost. To date, the card vendors providing card systems tend to encode the data on the chip via a separate station so this capability would not be required even at most institutions utilizing a chip card.
Will the printer accept only CR80 cards (standard ID size) or will it also print other sizes? Some card offices print badges for seminars and events onlarger cards.
In the past, desktop card printers could not print images that extended all the way to the edges of the card. These cards had a thin white band around the card. Many printers currently offer this full-bleed or edge-to-edge capability enabling more flexibility in the design of the card.
Depending upon the size of your card office the physical dimensions of the printer can make a difference in your workspace. Very compact printers are available today as well as the traditional large, heavy units
Ensure that the printer drivers (software) required for the specific printer you are considering are available for use with your card production system. If the drivers are not freely available, do not assume that the price to purchase them will be inconsequential. Some drivers can cost more than the price of a low-cost printer.
The price range for dye sub printers is extremely broad ranging from less than $1000 to more than $10,000. Examine your individual needs in terms of throughput and functionality before shopping for a printer.
A great way to begin the shopping process is to talk with integrators, vendors, andnend users. Manufacturer web sites can enable initial comparison shopping but the best information comes from peers who are actually using the printer.




